
Amazon CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront speeds up the distribution of static and dynamic web content such as html, css, php, images and media files. When users request content, CloudFront broadcasts it through a global network of Edge Locations that offer low latency and high performance.
Let us look at how it works in detail.
Presentation
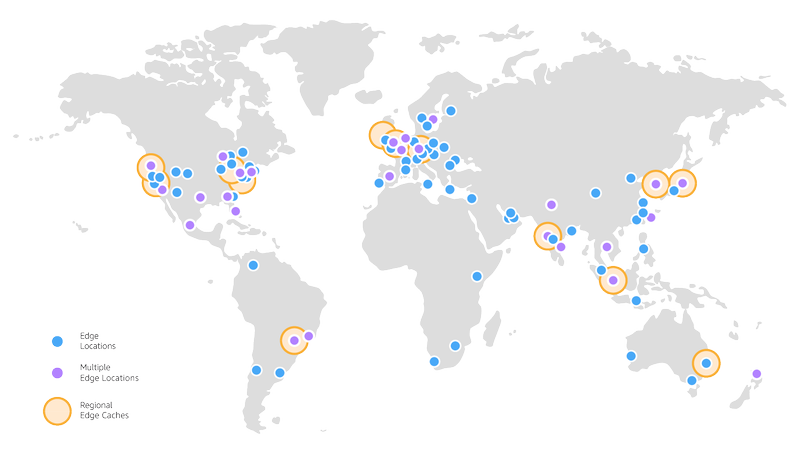
Amazon CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network (CDN), which is based on a system of Caches distributed over AWS’s 230 PoPs and interconnected via AWS backbone.
- CloudFront offers security features as:
- Network Attack Protection and anti-DDoS
- HTTPS Protocol *Field Level Encryption
- Integrates with AWS Shield, AWS Web Application Firewall and Amazon Route 53
- It works with any origin:
- All origins AWS Amazon S3 Bucket or WebSite, Amazon EC2, Elastic Load Balancing
- Any on-premise HTTP termination
Advanced mechanisms
CloudFront allows you to configure different Origins (Multiple Origins) depending on the content’s type content’s path (against pattern).
Similarly, an Origin Group consisting of Primary and Secondary Origins allows to set up a failover mechanism in case the Primary Origin returns an error.
Finally, there is an asymmetric field encryption mechanism (Field Level encryption) that allows a form field encryption from the Edge Location to the final HTTP endpoint which can decrypt the field.
Architectures
Depending on the origin, CloudFront integrates into 2 types of architecture.
S3 Bucket
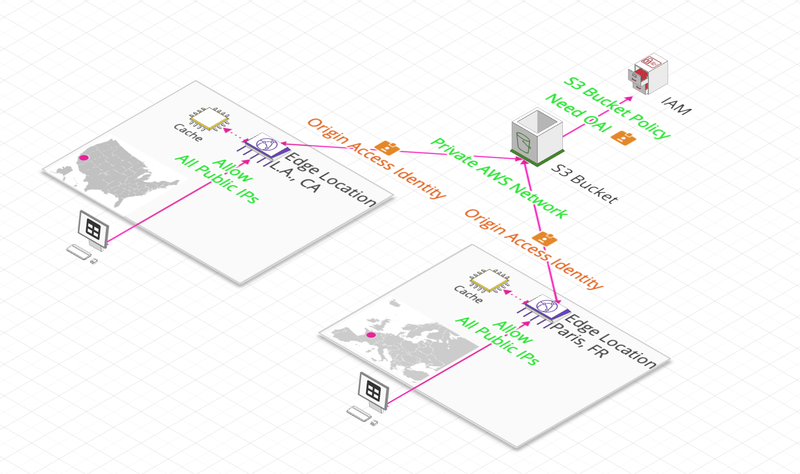
HTTP End-Point (ALB, EC2)
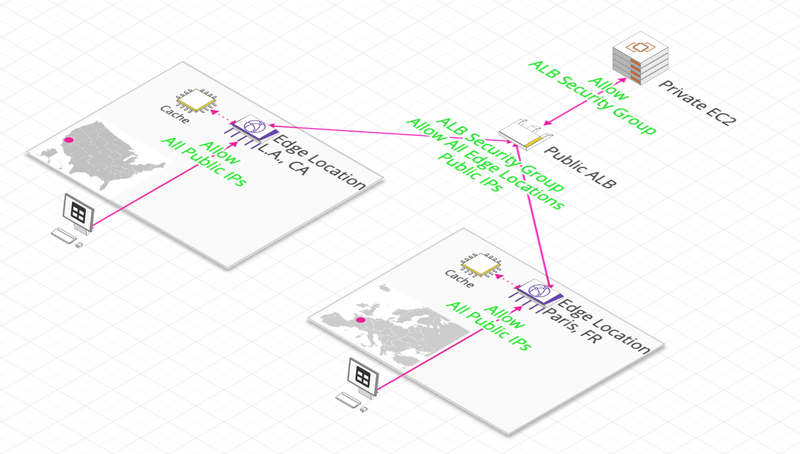
Security
Geo Restriction
CloudFront allows filter users by Country. A database linking IP addresses and country of membership allows only certain countries (whitelist) to access a resource or, on the contrary, blocks access to certain countries (blacklist)
HTTPS
CloudFront allows you to control the transport protocol used between the different points with Protocol Policy:
- Viewer Protocol Policy:
- From Customer to Edge Location
- Used to force HTTPS protocol or redirect HTTP calls to HTTPS
- Origin Protocol Policy:
- From Edge Location to Origin (S3 Bucket or HTTP Server)
- Allows you to choose between HTTP and HTTPS
Signed URL / Signed Cookie
This CloudFront functionality makes available content for a certain period of time:
- Signed URL: provides a file to any user with this URL
- Signed Cookie: makes several files available to any user who has this cookie
The validity time depends on the content you want to share:
- Paid content, 24 hour rental,…
- Storage space reserved for 1 year,…
Do not confuse CloudFront Signed URLs with S3 Pre-Signed URLs
Generating from Trusted Key Groups
Now, AWS recommends using Trusted Key Groups to generate Signed URL / Cookie. Indeed:
- Management (creation, rotation,…) of Trusted Key Groups is done entirely using AWS APIs
- The use of these APIs is protected by an IAM Role
A Trusted Key Groups consists of:
- A private key used to sign a URL or Cookie
- A public key used to verify that the signature is valid
CloudFront Caching
The content can be cached according to 3 different criteria:
- Header
- Session Cookie
- URL parameter
The Time To Live (TTL) can range from 0 sec to 1 year and depends on the type of content:
- For static content: TTL can be large because content does not change much and it is a good way to reduce latency. The criteria of Headers and Cookie should not be taken into account but only the URL.
- For dynamic content: TTL should be low and based on Headers and Cookies to maximize cache without the risk of delivering obsolete content.
It is also possible to disable specific content from caches (depending on patterns) so that all Edge Locations update their cache with the new content version.
Price Classes
Because there are more than 230 Edge Locations, the cost of CloudFront can quickly increase. It is possible to reduce this cost by selecting Edge Locations according to their price per Region.
There are 3 price classes that can be selected:
- Price Class All: all Regions, high cost but better performance
- Price Class 200: most Regions but removes those with the highest cost
- Price Class 100: cheapest Regions




