
AWS CI/CD: CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, and CodePipeline
When it comes to cloud application development, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a comprehensive range of tools that facilitate continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD). These essential processes enable development teams to deliver applications quickly and regularly with high quality.
In this article, we will explore the fundamental principles and key concepts of the following AWS development tools: CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, and CodePipeline. Each of these services plays a specific role in the lifecycle of an application and provides powerful features to automate various stages of development and deployment.
By understanding these services, you will be able to effectively utilize AWS’s continuous integration and continuous deployment tools, enabling you to accelerate development, improve code quality, and deploy applications reliably and consistently.
AWS CodeCommit
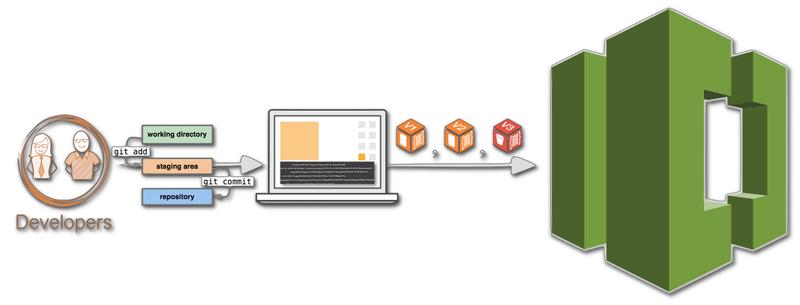
AWS CodeCommit is a Git-based version control service hosted by AWS. It provides a secure and scalable platform for storing and managing the source code, binary files, and documents of your projects in the cloud.
Key features of CodeCommit:
Code storage and management: CodeCommit allows you to easily store and manage the source code of your applications, as well as other types of files such as binary files or documents. You can organize your code repositories based on your projects and access them centrally.
Security and protected access: CodeCommit ensures the security of your resources through integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). You can define granular authorization policies to control access to the source code and repositories. This allows you to finely manage the permissions of users, groups, and roles within your organization.
High availability and automatic scaling: CodeCommit is a fully managed service by AWS, which means it offers high availability without any repository size limits. You don’t have to worry about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure. The service automatically scales to meet your storage and performance needs.
Data encryption and security: CodeCommit encrypts your data during transfers via HTTPS or SSH. Additionally, you can choose to encrypt the contents of your repositories using AWS Key Management Service (KMS). This ensures the confidentiality of your source code and files.
Trigger actions based on events: CodeCommit can trigger actions based on specific events. For example, you can configure notifications to Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), execute AWS Lambda functions, or trigger events in AWS CloudWatch Events. This allows you to automate actions in response to events related to your code repositories.
By using AWS CodeCommit, you gain a robust and secure service for managing your code versions, offering advanced features for authentication, authorization, encryption, and event-based action triggering.
Granting access to your repository
Use an IAM Role and grant access to your role using AWS Security Token Service (STS)
AWS CodeBuild
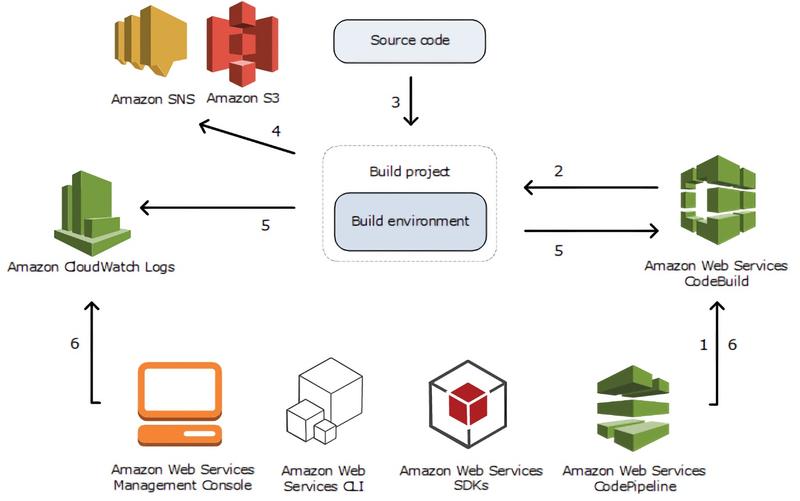
AWS CodeBuild is a service that facilitates code compilation and testing in the application development process. It offers seamless integration with various code sources, including CodeCommit, CodePipeline, GitHub, and S3.
Defining a Build
To define a build in CodeBuild, you use a configuration file called buildspec.yml. This file specifies the specific instructions to be executed during the application build process.
Here is an example structure of a buildspec.yml file:
version: 0.2
run-as: Linux-user-name
env:
shell: shell-tag
variables:
key: "value"
phases:
install:
commands:
- command
finally:
- command
pre_build:
commands:
- command
build:
run-as: Linux-user-name
on-failure: ABORT
commands:
- command
post_build:
commands:
- command
reports:
report-group-name-or-arn:
files:
- location
- location
base-directory: location
discard-paths: no | yes
file-format: report-format
artifacts:
files:
- location
name: artifact-name
s3-prefix: prefix
cache:
paths:
- pathenv: During the build definition, you have the flexibility to define environment variables to configure the behavior of the build. This allows you to customize the build process according to your specific needs.
phases: A build in CodeBuild is organized into different phases that define the steps of the build process. Here are some commonly used phases:
install: This phase is dedicated to installing dependencies and tools required for building your application. You can specify the commands and steps needed to set up the build environment.
pre_build: In this phase, you can perform preliminary actions before code compilation, such as configuring additional environment variables or running preparation scripts.
build: This is the main phase where the source code is compiled and transformed into an executable artifact. You can specify compilation commands, unit tests, validations, and other necessary build tasks.
post_build: After the successful build of the application, this phase allows you to perform additional actions such as packaging the application, generating reports, or archiving the generated artifacts.
artifacts: The artifacts generated during the build, such as binary files or packages, can be stored in an S3 bucket. This facilitates their retrieval or use in subsequent deployment steps.
cache: To speed up builds, CodeBuild supports caching of dependencies. This means that if a dependency has already been downloaded in a previous build, it can be retrieved from the cache instead of being downloaded again. This saves time and optimizes build performance.
Finally, CodeBuild offers the ability to launch a build locally using Docker. This feature is useful for debugging and troubleshooting build errors as it allows you to run the build process on your development machine.
Key Benefits of CodeBuild:
Fully managed service: CodeBuild does not require any provisioning of build servers. It is a fully managed service by AWS, allowing you to focus on developing your application without worrying about infrastructure management.
Auto-scalability and no limits: CodeBuild can handle variable workloads through its auto-scaling capability. It can run multiple builds simultaneously to accelerate the development process. Additionally, there are no predefined limits on project size or the number of builds.
Usage-based cost: You are only charged for the actual build time used. This enables flexible and cost-effective pricing based on your needs.
Customization of Docker images: CodeBuild relies on CloudWatch Events and AWS Lambda and uses Docker images to execute builds. You can customize these images to support different programming languages and specific dependencies for your project. Images exist for Java, Python, Ruby, Go, Node.js, PHP, .NET, and more.
Integration with security services: CodeBuild tightly integrates with other AWS security services such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for artifact encryption, IAM Roles for build permission management, VPC Network Security for running tests in your VPC, and AWS CloudTrail for logging API calls.
Integration within the AWS ecosystem: CodeBuild offers close integration with the AWS ecosystem, enhancing visibility and management of builds. Here are some key integration features:
Build logs can be stored in locations such as S3 or AWS CloudWatch, providing full traceability of build activities.
CodeBuild generates metrics that allow you to track build performance and gain insights into execution times, potential errors, and more.
With integration with CloudWatch Alarms, you can set up failure detection thresholds for builds. When these thresholds are reached, notifications are triggered to alert you of potential issues.
Using Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), CodeBuild can send customized notifications to inform team members or stakeholders about important build events.
With AWS CodeBuild, you have a powerful and flexible service to automate the compilation and testing of your code, benefiting from simplified management, usage-based pricing, and tight integration with other AWS services.
CodeBuild or CodePipeline
Build instructions can be defined in both CodeBuild and CodePipeline. It’s important to understand that defining these instructions in both tools can lead to unintended and difficult-to-interpret behaviors.
VPC
By default, CodeBuild runs outside of your VPC. To access resources such as a load balancer, a database, or an EC2 instance, you need to configure a VPC configuration (VPC ID, subnet IDs, security group ID).
AWS CodeDeploy
AWS CodeDeploy is an automated application deployment service that simplifies and automates the deployment process for a wide range of instances, including EC2 instances and Lambda functions.
When using CodeDeploy, it is necessary to install the CodeDeploy Agent on the target instances. This agent plays a key role in executing deployments and facilitates the coordination of deployment actions on the relevant instances.
CodeDeploy operates based on the use of a configuration file called appspec.yml. This file specifies detailed instructions for each deployment.
CodeDeploy organizes instances into groups, typically by environment (e.g., development, testing, production). This organization allows for consistent application deployments on specific target instances for each environment.
Here are some important terms to know in the context of CodeDeploy:
Application: The name of the application or application component you want to deploy.
Compute Platform: EC2 target instances, instances belonging to an Auto Scaling Group (ASG), on-premises instances, and Lambda functions.
- Deployment Configuration:
- For EC2 and on-premises instances, you can specify a minimum percentage of instances in a healthy state required for deployment.
- For Lambda functions, you can define traffic routing to the newly deployed versions.
Deployment Type: CodeDeploy supports In-Place deployments (updating the application on existing instances) as well as Blue/Green deployments, which involve launching new EC2 instances and bringing them into service before switching traffic to them.
IAM Instance Profile: IAM permissions for EC2 instances to read artifacts from S3 or GitHub during deployment.
Application Revision: The source code revision and
appspec.ymlfile.Service Role: An IAM role that allows CodeDeploy to perform necessary actions for deployment.
- Target Revision: The version of the application once the deployment process is completed.
Defining a deployment in CodeDeploy involves several key elements:
File Section: Instructions for copying the artifact from S3 to the file system of each target instance.
Hooks: Instructions for deploying the new version of the application on the instances. Hooks are divided into different ordered phases, including:
- ApplicationStop: Stopping the currently running application on the target instances.
- DownloadBundle: Downloading the new version of the application from S3.
- BeforeInstall: Performing specific actions before installing the new version.
- Install: Installing the new version of the application.
- AfterInstall: Performing additional actions after installation.
- ApplicationStart: Starting the new version of the application.
- ValidateService: Checking the functionality of the new version of the application using a health check.
In the case of Blue/Green deployments with EC2 instances, CodeDeploy allows for launching new EC2 instances, deploying the new version of the application on those instances, bringing them into service, and switching traffic to them while retaining the previous version of active instances for possible rollback.
AWS CodeDeploy offers a comprehensive solution for automated application deployment on various platforms and configurations, providing flexibility and ease of use for continuous deployment.
AWS CodeStar
AWS CodeStar is an integrated CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) solution offered by AWS. It brings together a set of services and tools that facilitate application development and deployment.
CodeStar provides a comprehensive overview of CI/CD services and allows for their management from a single entry point. This simplifies the configuration and management of the entire development process, from source code to application delivery.
One of the key features of CodeStar is its integration of CI/CD services with other popular tools. For example, certain regions offer integration with the Cloud9 IDE, a cloud-based development environment, as well as with JIRA or GitHub Issues, ticket management tools. This integration allows developers to access these tools from the same dashboard and benefit from a smoother development experience.
CodeStar also offers a development and CI/CD environment tailored to the application’s language. Whether you are using Java, Go, Python, Node.js, HTML5, or other languages, CodeStar provides templates and preconfigured settings to facilitate the creation of an appropriate development environment. This saves time and simplifies the initial setup by providing a project structure tailored to the chosen language.
AWS CodePipeline
AWS CodePipeline is an orchestration service for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) offered by AWS. It enables the setup and management of fully automated deployment pipelines.
CodePipeline acts as an orchestrator to coordinate the different stages of the deployment process, from source code retrieval to application delivery. It facilitates continuous integration by automating build, testing, and subsequent deployments, ensuring fast and reliable application delivery.
CodePipeline offers seamless integration with third-party tools such as GitHub, Jenkins, and AWS services like Elastic Beanstalk, CloudFormation, and ECS. This allows developers to use their preferred tools and easily integrate them into their deployment pipelines.
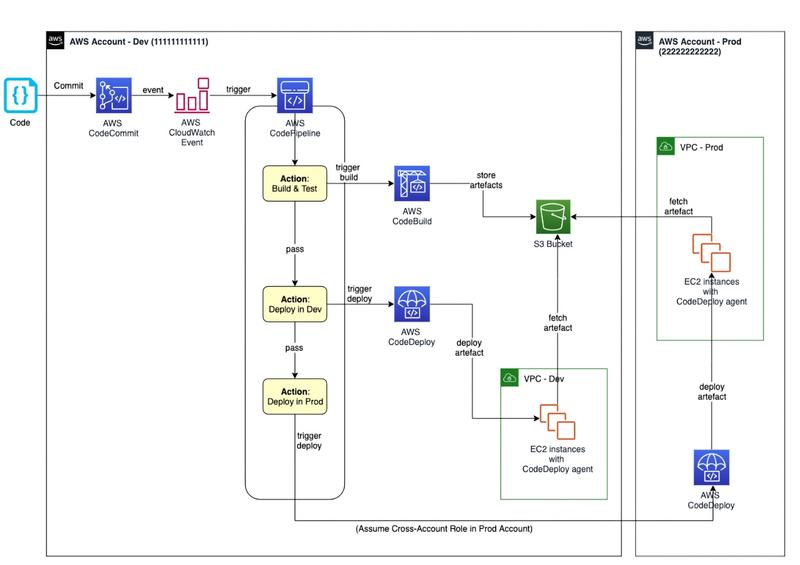
A concrete example of implementing a CI/CD pipeline with CodePipeline could look like this:
The developer pushes code to CodeCommit.
An event is triggered to AWS CloudWatch Event, which automatically triggers AWS CodePipeline. It initiates the build process using AWS CodeBuild. The source code is retrieved, compiled, tested, and artifacts are delivered to an S3 bucket.
AWS CodePipeline then triggers a deployment with AWS CodeDeploy, which launches the deployment of applications on EC2 instances using the previously installed CodeDeploy Agent.
This implementation scenario demonstrates how CodePipeline can orchestrate the entire CI/CD process, from source code management to application delivery, by automating the different steps and facilitating integration with various tools and services. Of course, there are more complex scenarios involving other AWS or external services.
In summary, AWS CodePipeline is a powerful tool for orchestrating CI/CD pipelines. It provides flexibility and ease of use, allowing developers to create automated and customizable deployment workflows while integrating third-party tools and AWS services to meet the specific needs of their development process.
Conclusion
We encourage you to further explore each service and use them in real projects. Each of these tools has its own features and benefits, and by using them appropriately, you can accelerate development, improve application quality, and optimize your deployment processes on AWS.
In summary, with AWS CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, and CodePipeline, you have a set of powerful tools for application development and deployment on AWS. By mastering them, you can create efficient workflows and enhance your entire development process.




