
Storage for AWS EC2 Instances
Here we will see the different storage services that can be used by an EC2 instance as well as their characteristics and their use cases.
EBS Volume
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) is a web service that provides block level storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. EBS volumes are highly available and reliable storage volumes that can be used as hard drive.
- It’s a Network drive:
- It uses the network to communicate with the instance
- There might be a bit of latency
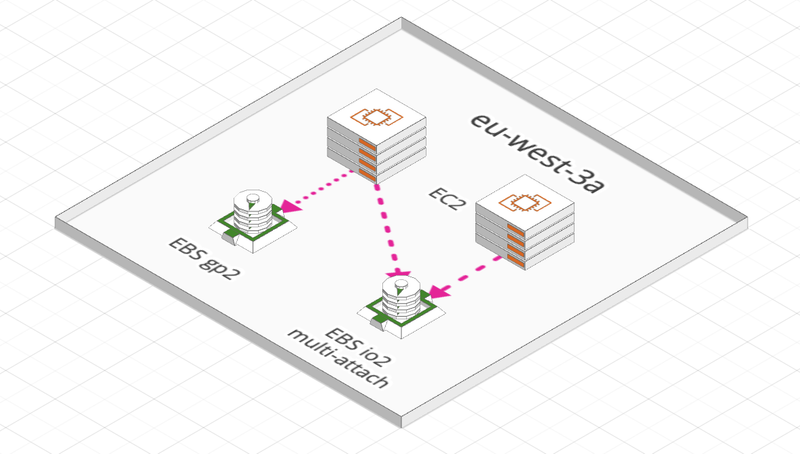
- Can be dettached and attached quickly while the instance is running
- Can only be mounted to one instance at a time (except for multi-attached - see bellow)
- It’s locked to a specific Availibility Zone:
- You could not bound to an instance whitin another A.Z.
- But you can snapshot it and copy it to another A.Z.
- It can be deleted or not after instance termination:
- So data can be persistent or not
Types of EBS
gp2 or gp3 (SSD):
- General purpose SSD volume with a balanced price and performance
- 1 Gib to 16 TiB
- gp2:
- IOPS is linked with the volume size
- Max IOPS is 16,000 at 5,333 GiB
- Small volume size can burst to 3,000
- gp3:
- IOPS starts at 3,000
- IOPS and throughput can increase independently up to 16,000 and 1000 MiB/s
- Use cases: Boot volume, non-Prod environment
io1 or io2 (SSD) or Provisioned IOPS SSD (PIOPS)
- The Highest performance SSD for low-latency and high-throughput workloads
- Supports EBS Multi-attach
- io1 / io2:
- 4 GiB to 16 TiB
- Max IOPS 64,000 with Nitro EC2 otherwise 32,000 with others instance type
- PIOPS can increase independently of storage size
- io2 Block Express:
- 4 GiB to 64 TiB
- Sub-millisecond latency
- Max PIOS 256,000 with IOPS:GiB ratio of 1000:1 (that means max PIOPS is reached from 256 GiB)
- Use cases: Databases
st1 (HDD) or Throughput Optimized:
- Low cost HDD volume designed for frequently accessed and throughput intensive workloads
- Can NOT be a Boot volume
- 125 MiB to 16 TiB
- Max IOPS is 500 and throughput 500 MiB/s
- Use cases: Big Data, Data Warehouse, Log Processing
sc1 (HDD) or Cold HDD:
- The Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads
- Can NOT be a Boot volume
- 125 MiB to 16 TiB
- Max IOPS is 250 and throughput 250 MiB/s
- Use cases: Data that is infrequently accessed where lower cost is important
EBS Multi-attach
- Only for io1 and io2 family
- You can attach the same EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances within the same A.Z.
- Each instance has full read / write permissions to the volume
- But must use a clustered file system to preserve data consistency
EFS
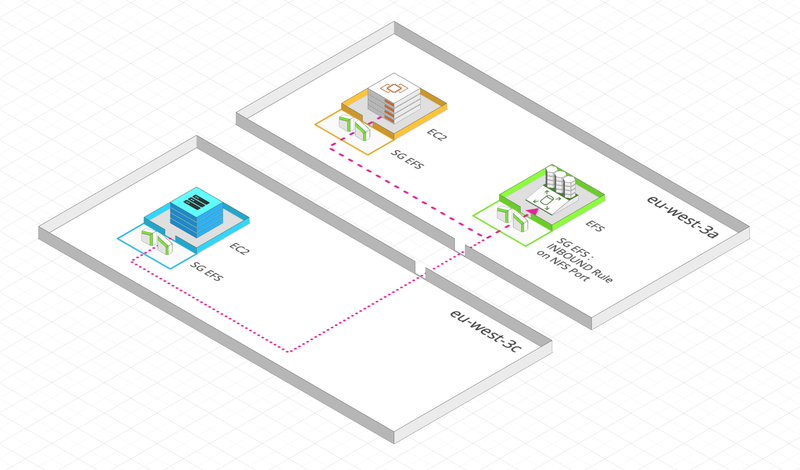
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides file storage for your Amazon EC2 instances. It’s a managed NFS (Network File System) that can be mounted to multiple EC2 instances:
- It’s increasing automatically, so you don’t have to provision anything and you pay-per-use
- Is multi-AZ
- You have to use Security Group to access to EFS
- Uses NFSv4.1 protocol and is only compatible with POSIX Operating System (including Linux, macOS but not Windows)
- Use cases: Content management, web server, data sharing.
Modes and classes
- Scaling:
- 100s of concurrent NFS clients with 10+ GiB/s throughput
- Can grow to Petabyte
- Performance mode:
- General Purpose: latency sensitive apps like web server, CMS, …
- Max I/O: higher latency, throughput but highly parallel : Big Data, Media Processing, …
- Throughput mode:
- Bursting: depends on the storage size (e.g. 1 TB = 50 MiB/s with burst up to 100 MiB/s)
- Provisioned: you set your desired throughput (e.g; 1 TB with 1 GiB/s)
- Storage Tiers:
- Standard: for frequently accessed files
- Infrequent Access: move file after n-days to EFS-IA which costs less but cost to retrieve the files
Instance Store
- Hight performance harware disk with high I/O
- But ephemeral:
- Data is lost when the instance is stopped
- You have to manage backup and restoration yourself if you don’t want it to be deleted
- Good for cache, buffer and temporary data




