Turn Your Nginx Server into a Fortress with Fail2ban and UFW
In today’s digital world, web server security is not just an option, but an absolute necessity. In an era where cyber attacks are multiplying and constantly evolving, effectively protecting one’s online infrastructure has become paramount. This article focuses on securing a Nginx web server, a platform widely used for its reliability and performance.
We will address two essential tools in the arsenal of computer security: Fail2ban and UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall). Fail2ban is an intrusion prevention software that protects your server against unauthorized access attempts, often marked by multiple failed login attempts. On the other hand, UFW offers simplified firewall management, allowing easy control of incoming and outgoing traffic.
In this article, we will detail how these tools can be used together to enhance the security of your Nginx server. We will explore the steps of installation and configuration, guiding you through the process of setting up effective security rules.
- Introduction to Fail2ban and UFW
- Basic Installation and Configuration
- Advanced Configuration of UFW
- Advanced Configuration of Fail2ban
- Visualization and Analysis of Bans
- Conclusion
Introduction to Fail2ban and UFW
Fail2ban: The Digital Bodyguard
Fail2ban is an indispensable tool for server security. Its primary role is to monitor your server’s logs for signs of malicious activities, especially repeated unsuccessful login attempts. By detecting these attempts, often indicative of a brute-force attack, Fail2ban intervenes by temporarily banning the attacker’s IP address, thereby quarantining it to prevent future intrusions.
This software operates through “filters” defined by the user, which specify the conditions under which an IP address should be banned. These filters are associated with “actions”, such as modifying firewall rules to block traffic from the banned address. Thus, using Fail2ban is a proactive method to protect your server against common attacks, while remaining flexible enough to adapt to various threat scenarios.
UFW: A Simplified Firewall Approach
UFW, standing for Uncomplicated Firewall, is an easy-to-use firewall for Linux-based operating systems. True to its name, UFW aims to simplify firewall management while offering robust protection. It serves as a user interface for iptables, the default firewall in Linux.
With UFW, you can easily set up rules that determine which traffic is allowed to enter or leave your server. These rules can be defined based on ports, protocols, and IP addresses. UFW also allows for the configuration of more complex rules if necessary, while maintaining a simple interface for less experienced users.
Essential Complementarity
The combination of Fail2ban and UFW provides a solid layer of security for your Nginx server. While Fail2ban focuses on preventing brute-force attacks by banning suspicious IPs, UFW manages overall inbound and outbound traffic, thus offering a barrier against a wide range of threats. By using these two tools together, you create a server environment that is not only resistant to the most common attacks but also adaptable to emerging threats.
Basic Installation and Configuration

While the following instructions are specific to Ubuntu Linux distribution, the principles and commands are largely transferable to other Linux systems. With minor adaptations, these steps can be applied to various distributions, making this guide useful for a wide range of Linux users.
Step 1: Installing UFW
- 1. Install UFW: To install UFW, run:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ufwStep 2: Installing Fail2ban
- 1. Install Fail2ban: Execute the following commands to install Fail2ban on your Ubuntu server:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install fail2ban- 2. Activate the Fail2ban service: To start the service and enable it automatically at system startup, run the following commands:
sudo systemctl start fail2ban
sudo systemctl enable fail2ban- 3. Verify the installation: To ensure that the service has started and is functioning correctly, launch:
sudo systemctl status fail2banYou should see:
● fail2ban.service - Fail2Ban Service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/fail2ban.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2023-12-22 00:16:31 CET; 1 day 9h ago
Docs: man:fail2ban(1)
Main PID: 601234 (fail2ban-server)
Tasks: 19 (limit: 11829)
Memory: 39.8M
CPU: 2h 43min 80ms
CGroup: /system.slice/fail2ban.service
└─601234 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/fail2ban-server -xf start
Dec 22 00:16:31 myserver systemd[1]: Started Fail2Ban Service.
Dec 22 00:16:32 myserver fail2ban-server[601234]: Server readyStep 3: Understanding How Fail2ban Works
Before delving into configuration, it is crucial to understand how Fail2ban operates. This software relies on three main components located in different directories: jails, filters, and actions.
1. Jails: These are sets of rules defining when and how an IP address should be banned. A jail is defined by log files to monitor, using filters (in the form of regex), and triggers actions when failures are detected (the filters return a result).
Fail2ban includes predefined jail configurations in
/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf.2. Filters: They are used to analyze service logs via regex to detect suspicious behavior, such as intrusion attempts.
They are found in
/etc/fail2ban/filter.d/.3. Actions: These can include banning an IP address, sending notifications, or executing custom scripts.
The actions, defining commands to ban or unban an IP address, are located in
/etc/fail2ban/action.d/.
Step 4: Configuring Fail2ban’s Basic Rules
Warning
Do not directly modify the files /etc/fail2ban/fail2ban.conf and /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf: these files, containing fail2ban’s default configurations, can be reset during system updates.
- 1. Create a dedicated configuration file: To do this, open your favorite editor, here nano, by executing the command:
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.d/custom.conf- 2. Override the base configurations: All default parameters and configurations are found in the file
/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf. Here is a list of important parameters to override and adapt according to the behavior you desire:- bantime: Defines the duration of an IP ban (default 10 minutes, recommended several hours or days).
- findtime: Period during which anomalies are searched for in the logs.
- ignoreip: List of IPs to ignore, including yours to avoid self-banning.
- maxretry: Number of failed attempts allowed before banning.
Also define the use of UFW to take control of the banning (
banactionandbanaction_allports).Here is an example of a drastic configuration, banning any first intrusion attempt for 1 day. We also define the use of UFW, (note the local IP addresses that you may need to adjust according to your local network configuration):
[DEFAULT]
bantime = 1d
findtime = 1d
ignoreip = 127.0.0.1/8 192.168.0.0/16
maxretry = 1
banaction = ufw
banaction_allports = ufw- 3. Restart the Fail2ban service: To apply your modifications, restart the Fail2ban service by launching the command:
sudo systemctl restart fail2ban- 4. Verify the service status:
sudo fail2ban-client statusWhich should give you:
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
Status
|- Number of jail: 1
`- Jail list: sshdAdvanced Configuration of UFW
We will apply the principle of least privilege by defaulting to blocking all incoming and outgoing connections, and only allowing the necessary traffic for specific services. By following this principle, we minimize the risks associated with unauthorized access or exploitation of vulnerabilities, ensuring that only essential ports and services are accessible.
Let’s see how to configure the firewall rules with UFW:
Step 5: Block Everything and Open Only What’s Necessary
- Setting default rules: Block all incoming and outgoing connections by default:
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default deny outgoingAuthorizing necessary connections: Open HTTP and HTTPS ports in both directions, SSH, and outgoing DNS:
- Allow incoming connections for the web (HTTP and HTTPS):
sudo ufw allow in 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow in 443/tcp- Allow outgoing connections for the web:
sudo ufw allow out 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow out 443/tcp- Allow SSH connections (for remote management):
sudo ufw allow in 22/tcp- Allow outgoing DNS connections (for domain name resolution):
sudo ufw allow out 53/udpStep 6: Activating the Rules
- Activating the UFW firewall: Enable UFW with:
sudo ufw enable- Checking the configured rules: Recheck the status and rules of the firewall with:
sudo ufw status verboseStep 7: Add Additional Rules Based on Your Services
- Mail: Allow outgoing SMTP connections for sending emails:
sudo ufw allow out 25/tcpAdditional Security (optional):
- Limit SSH connection attempts to enhance security:
sudo ufw limit 22/tcp comment 'Allow 6 connections over 30 seconds'- Restrict SSH access to certain IP addresses:
sudo ufw delete allow in 22/tcp
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.0.0/16 to any port 22 proto tcpAdvanced Configuration of Fail2ban
Step 8: List Preconfigured Filters on Your Server
- Nginx Filters: List existing filters (may differ on your server):
sudo ls -alt /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 327 Nov 23 2020 /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-sslerror.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 232 Nov 23 2020 /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-4xx.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 564 Nov 23 2020 /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-forbidden.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 681 Nov 23 2020 /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-botsearch.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 485 Nov 23 2020 /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-http-auth.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1454 Nov 23 2020 /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-limit-req.confCreate Filters: Create filters that do not exist on your server. For this, enter the commands:
- For the
nginx-sslerror.conffilter: This filter protects against SSL handshake failure attacks, where an attacker tries to negotiate an SSL/TLS connection with incorrect or malicious parameters.
- For the
sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-sslerror.conf <<EOF
[Definition]
failregex = SSL_do_handshake\(\) failed .+ while SSL handshaking, client: <HOST>, server: .+
ignoreregex =
datepattern = {^LN-BEG}%%ExY(?P<_sep>[-/.])%%m(?P=_sep)%%d[T ]%%H:%%M:%%S(?:[.,]%%f)?(?:\s*%%z)?
^[^\[]*\[({DATE})
{^LN-BEG}
EOF'- For the
nginx-4xx.conffilter: This filter detects requests generating HTTP 4xx errors (like 404, 403, 400), often the result of attempts to access unauthorized or non-existent resources, indicating malicious probing.
sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-4xx.conf <<EOF
[Definition]
failregex = ^<HOST>.*"(GET|POST).*" (404|444|403|400) .*$
ignoreregex = .*(robots.txt|favicon.ico|jpg|png)
EOF'- For the
nginx-forbidden.conffilter: This filter targets attempts to access forbidden directories. It is useful for blocking directory scans attempting to discover hidden files or folders on the server.
sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-forbidden.conf <<EOF
[Definition]
failregex = directory index of .+ is forbidden, client: <HOST>, server: .+
ignoreregex =
EOF'- For the
nginx-botsearch.conffilter: This filter focuses on requests for URLs that do not exist (404 errors), often a sign of a bot or scanner trying to find vulnerabilities or hidden pages.
sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-botsearch.conf <<EOF
# Fail2Ban filter to match web requests for selected URLs that don't exist
#
[INCLUDES]
# Load regexes for filtering
before = botsearch-common.conf
[Definition]
failregex = ^<HOST> \- \S+ \[\] \"(GET|POST|HEAD) \/<block> \S+\" 404 .+$
^ \[error\] \d+#\d+: \*\d+ (\S+ )?\"\S+\" (failed|is not found) \(2\: No such file or directory\), client\: <HOST>\, server\: \S*\, request: \"(GET|POST|HEAD) \/<block> \S+\"\, .*?$
ignoreregex =
datepattern = {^LN-BEG}%%ExY(?P<_sep>[-/.])%%m(?P=_sep)%%d[T ]%%H:%%M:%%S(?:[.,]%%f)?(?:\s*%%z)?
^[^\[]*\[({DATE})
{^LN-BEG}
# DEV Notes:
# Based on apache-botsearch filter
#
# Author: Frantisek Sumsal
EOF'- For the
nginx-http-auth.conffilter: This filter is used to detect and block repeated failed authentication attempts, indicating a possible brute-force attack on password-protected areas.
sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-http-auth.conf <<EOF
# fail2ban filter configuration for nginx
[Definition]
failregex = ^ \[error\] \d+#\d+: \*\d+ user "(?:[^"]+|.*?)":? (password mismatch|was not found in "[^\"]*"), client: <HOST>, server: \S*, request: "\S+ \S+ HTTP/\d+\.\d+", host: "\S+"(?:, referrer: "\S+")?\s*$
ignoreregex =
datepattern = {^LN-BEG}
# DEV NOTES:
# Based on samples in https://github.com/fail2ban/fail2ban/pull/43/files
# Extensive search of all nginx auth failures not done yet.
#
# Author: Daniel Black
EOF'- For the
nginx-limit-req.conffilter: This filter aims to block IP addresses that exceed the request limits defined in Nginx (limit_req), typical of a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack or aggressive bot behavior.
sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/nginx-limit-req.conf <<EOF
# Fail2ban filter configuration for nginx :: limit_req
# used to ban hosts, that were failed through nginx by limit request processing rate
#
# Author: Serg G. Brester (sebres)
#
# To use 'nginx-limit-req' filter you should have `ngx_http_limit_req_module`
# and define `limit_req` and `limit_req_zone` as described in nginx documentation
# http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_limit_req_module.html
#
# Example:
#
# http {
# ...
# limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=lr_zone:10m rate=1r/s;
# ...
# # http, server, or location:
# location ... {
# limit_req zone=lr_zone burst=1 nodelay;
# ...
# }
# ...
# }
# ...
#
[Definition]
# Specify following expression to define exact zones, if you want to ban IPs limited
# from specified zones only.
# Example:
#
# ngx_limit_req_zones = lr_zone|lr_zone2
#
ngx_limit_req_zones = [^"]+
# Use following full expression if you should range limit request to specified
# servers, requests, referrers etc. only :
#
# failregex = ^\s*\[[a-z]+\] \d+#\d+: \*\d+ limiting requests, excess: [\d\.]+ by zone "(?:%(ngx_limit_req_zones)s)", client: <HOST>, server: \S*, request: "\S+ \S+ HTTP/\d+\.\d+", host: "\S+"(, referrer: "\S+")?\s*$
# Shortly, much faster and stable version of regexp:
failregex = ^\s*\[[a-z]+\] \d+#\d+: \*\d+ limiting requests, excess: [\d\.]+ by zone "(?:%(ngx_limit_req_zones)s)", client: <HOST>,
ignoreregex =
datepattern = {^LN-BEG}
EOF'Step 9: Add Jails to Your Configuration
To add these jails to the Fail2Ban configuration in the custom.conf file, follow these steps:
- Open the configuration file: Use the command to open the file in a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.d/custom.conf- Add jail configurations: Copy and paste the following configurations at the end of the file:
[sshd]
enabled = true
[nginx-4xx]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = nginx-4xx
logpath = %(nginx_error_log)s
[nginx-http-auth]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = nginx-http-auth
logpath = %(nginx_error_log)s
[nginx-botsearch]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = nginx-botsearch
logpath = %(nginx_access_log)s
[nginx-forbidden]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = nginx-forbidden
logpath = %(nginx_error_log)s
[nginx-sslerror]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = nginx-sslerror
logpath = %(nginx_error_log)s
[ufw]
enabled = true
filter = ufw
logpath = /var/log/ufw.logSave and close the file: After adding the configurations, save the file and close the text editor.
Restart Fail2Ban: To apply the changes, restart Fail2Ban with:
sudo systemctl restart fail2banThis configuration will add and activate the specified jails for SSH, various Nginx configurations, and UFW.
Step 10: Verification and Testing
After configuring, it is essential to test and verify that everything is working correctly.
- Checking Fail2ban: Use this command to list the active jails and check that Fail2ban is functioning properly.
sudo fail2ban-client statusWhich returns:
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
Status
|- Number of jail: 7
`- Jail list: nginx-4xx, nginx-botsearch, nginx-forbidden, nginx-http-auth, nginx-sslerror, sshd, ufwThese steps form the basis for securing your Nginx server on Linux with Fail2ban and UFW. Remember that the configuration can be customized according to the specific needs of your server and network.
You will find multiple filters for Fail2ban on the internet, tailored to the services running on your server.
Visualization and Analysis of Bans

Data Extraction
To effectively understand and analyze Fail2Ban’s security actions, it’s useful to have an overview of the banned IP addresses.
The following script provides this visibility, categorized by jail:
for jail in $(sudo fail2ban-client status | grep 'Jail list:' | sed 's/.*://;s/,//g'); do
echo "Jail: $jail";
sudo fail2ban-client status $jail | grep 'Banned IP';
doneHere is an example of all the IPs that have been blocked on my server:
Jail: nginx-4xx
`- Banned IP list:
Jail: nginx-botsearch
`- Banned IP list: 199.229.240.163
Jail: nginx-forbidden
`- Banned IP list: 104.199.31.214 146.190.242.134 152.32.211.69 159.203.88.161...
Jail: nginx-http-auth
`- Banned IP list:
Jail: nginx-sslerror
`- Banned IP list: 107.170.208.31 167.248.133.182 212.102.40.218
Jail: sshd
`- Banned IP list: 101.34.23.155 101.43.39.167 103.144.3.14 103.39.209.130 103...
Jail: ufw
`- Banned IP list: 192.241.233.7 1.12.249.176 1.12.73.13 1.21.202.235 1.34.233...I truncated the IPs, there were more than 2600 for 24 hours of retention! This example shows that a very large number of IP addresses were blocked on my server, which does not contain highly sensitive data.
The significant volume of banned IPs also highlights the extent and consistency of automated attacks against online servers. Even systems that seem uninteresting are frequently targeted by bots and cyber attackers seeking vulnerabilities, for malicious purposes such as spam or botnet creation. There are also many legitimate companies scanning the internet for compromised servers.
Calculating Some Statistics
The analysis of IP data can reveal significant information about the geographical distribution, organizational ownership, and location of these scans.
The Bash script below allows for precise statistics to be calculated from the collected IP addresses. These statistics include the counting of the number of IP addresses by country, organization, and city. This process helps understand the trends of attacks and their geographic distribution.
#!/bin/bash
# Replace this with your personal API key to the free service https://ipinfo.io
API_KEY="your_api_key_here"
# Name of the file containing IP addresses (one per line)
FILE="ip_list.txt"
# Files for storing counts
COUNTRY_FILE="country_count.txt"
ORG_FILE="org_count.txt"
CITY_FILE="city_count.txt"
# Initialize counting files if they do not exist
> "$COUNTRY_FILE"
> "$ORG_FILE"
> "$CITY_FILE"
# Function to obtain geolocation information of an IP address
get_ip_info() {
local ip=$1
curl -s "https://ipinfo.io/$ip?token=$API_KEY"
}
# Check if the file exists
if [ ! -f "$FILE" ]; then
echo "File $FILE not found."
exit 1
fi
# Iterate over each line in the file
while IFS= read -r ip
do
echo "Processing ${ip}..."
ip_info=$(get_ip_info "$ip")
country=$(echo "$ip_info" | jq -r '.country')
org=$(echo "$ip_info" | jq -r '.org')
city=$(echo "$ip_info" | jq -r '.city')
# Update counting files
echo "$country" >> "$COUNTRY_FILE"
echo "$org" >> "$ORG_FILE"
echo "$city" >> "$CITY_FILE"
done < "$FILE"
# Function to count occurrences
count_occurrences() {
sort -bfg | uniq -c
}
# Function to sort occurrences
sort_occurrences() {
sort -rn -k1,1
}
# Display statistics
echo "Statistics by country code:"
cat "$COUNTRY_FILE" | count_occurrences | sort_occurrences
echo "Statistics by organization:"
cat "$ORG_FILE" | count_occurrences | sort_occurrences
echo "Statistics by city:"
cat "$CITY_FILE" | count_occurrences | sort_occurrencesScans by Country
Results
1055 US
361 CN
252 GB
135 NL
98 DE
71 BR
69 TW
57 KR
53 IN
45 BE
44 RU
43 FR
40 JP
25 VN
24 HK
21 SG
20 IT
19 CA
16 BG
13 TR
13 TH
13 SE
13 ID
13 AU
11 AR
9 PL
7 UA
7 PH
7 LT
7 IR
5 IL
4 MX
4 CL
3 VE
3 RO
3 NG
3 IQ
3 CZ
2 GR
2 ES
2 CO
2 CH
2 BD
2 AT
2 AE
1 ZA
1 SK
1 SA
1 PK
1 PE
1 PA
1 NO
1 MY
1 MG
1 MA
1 LU
1 KZ
1 GU
1 DK
1 CV
1 CR
1 BZ
1 BY
1 BO
1 AZInterpretation of Blocked Scans by Country
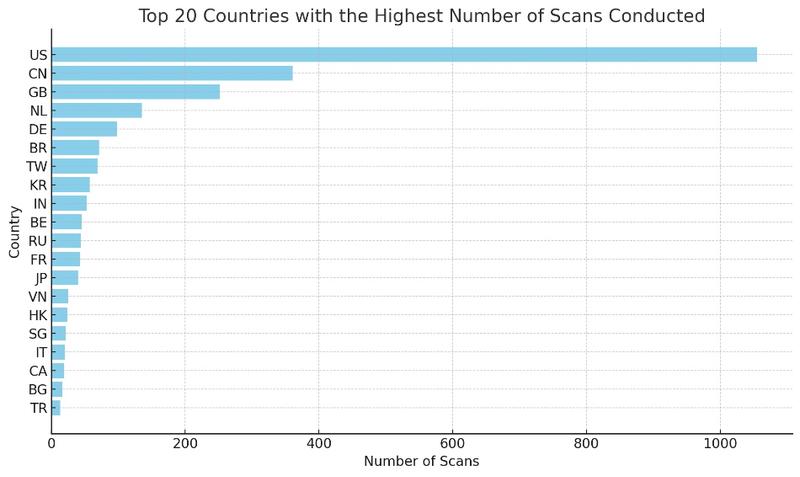
- 1. High Scanning Activity in the United States (US)
- Number of occurrences: 1055
- Implication: This high activity suggests a significant presence of scans, possibly automated, originating from the United States. This could indicate either a large number of active servers and computer systems or the presence of compromised networks.
- 2. Notable Presence of China (CN) and the United Kingdom (GB)
- China: 361 occurrences
- United Kingdom: 252 occurrences
- Implication: High frequency of scans from these regions, possibly indicating malicious activities or strong cyber defense.
- 3. Scans Originating from Europe
- Countries involved: Netherlands, Germany, Belgium, France, Russia
- Implication: Active scanning activities or networks often targeted by attacks, necessitating proactive defense.
- 4. Diversity of Asian Sources
- Countries involved: Taiwan, South Korea, India, Japan, Vietnam
- Implication: Regions active in scanning or targeted by attacks, reflecting the trends in cyber security in Asia.
- 5. Activity in Latin America and Africa
- Latin America: Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Colombia
- Africa: Less prevalent but notable presence
- Implication: Trend towards the automation of attacks or the presence of compromised systems in these regions.
- 6. Countries with Few Occurrences
- Examples: African countries, European and Asian countries with a single or very few counts
- Implication: Sporadic scanning attempts or isolated actors.
These statistics provide an insight into trends in cyber security and malicious activities on the Internet. They reveal the effectiveness of security measures like Fail2Ban and UFW in protecting a server from unauthorized or malicious access attempts.
Scans by Organization
Results
590 AS396982 Google LLC
384 AS14061 DigitalOcean, LLC
165 AS6939 Hurricane Electric LLC
108 AS4134 CHINANET-BACKBONE
98 AS398324 Censys, Inc.
71 AS37963 Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd.
59 AS45090 Shenzhen Tencent Computer Systems Company Limited
54 AS4837 CHINA UNICOM China169 Backbone
47 AS398705 Censys, Inc.
46 AS135377 UCLOUD INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY (HK) LIMITED
36 AS4766 Korea Telecom
35 AS132203 Tencent Building, Kejizhongyi Avenue
34 AS9829 National Internet Backbone
34 AS63949 Akamai Connected Cloud
27 AS16276 OVH SAS
24 AS51396 Pfcloud UG
24 AS211298 INTERNET MEASUREMENT
24 AS202425 IP Volume inc
24 AS198465 BtHoster LTD
21 AS394711 Limenet
17 AS20052 Arbor Networks, Inc.
17 AS10439 CariNet, Inc.
16 AS4713 NTT Communications Corporation
15 AS9009 M247 Europe SRL
15 AS211680 NSEC - Sistemas Informaticos, S.A.
13 AS58466 CHINANET Guangdong province network
12 AS51167 Contabo GmbH
12 AS3462 Data Communication Business Group
12 AS12876 SCALEWAY S.A.S.
10 AS9808 China Mobile Communications Group Co., Ltd.
10 AS36352 ColoCrossing
10 AS13213 UK-2 Limited
9 AS45102 Alibaba (US) Technology Co., Ltd.
8 AS7552 Viettel Group
8 AS50360 Tamatiya EOOD
8 AS36007 Kamatera, Inc.
8 AS34534 Harmony Hosting SARL
7 AS57523 Chang Way Technologies Co. Limited
7 AS21859 Zenlayer Inc
7 AS209605 UAB Host Baltic
7 AS198953 Proton66 OOO
6 AS174 Cogent Communications
6 AS140292 CHINATELECOM Jiangsu province Suzhou 5G network
5 AS49870 Alsycon B.V.
5 AS49581 Ferdinand Zink trading as Tube-Hosting
5 AS4808 China Unicom Beijing Province Network
5 AS3269 Telecom Italia S.p.A.
5 AS210644 AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD
5 AS204428 SS-Net
5 AS149621 SB Secure Data centers India Private Limited
5 AS10617 SION S.A
4 AS9121 Turk Telekomunikasyon Anonim Sirketi
4 AS8151 UNINET
4 AS7018 AT&T Services, Inc.
4 AS701 Verizon Business
4 AS53667 FranTech Solutions
4 AS23969 TOT Public Company Limited
4 AS208843 Alpha Strike Labs GmbH
4 AS207812 DM AUTO EOOD
4 AS201814 MEVSPACE sp. z o.o.
4 AS20001 Charter Communications Inc
4 AS19318 Interserver, Inc
4 AS140803 HQDATA
3 AS9318 SK Broadband Co Ltd
3 AS8075 Microsoft Corporation
3 AS7303 Telecom Argentina S.A.
3 AS714 Apple Inc.
3 AS58461 CT-HangZhou-IDC
3 AS5607 Sky UK Limited
3 AS4812 China Telecom (Group)
3 AS45899 VNPT Corp
3 AS398101 GoDaddy.com, LLC
3 AS38365 Beijing Baidu Netcom Science and Technology Co., Ltd.
3 AS33491 Comcast Cable Communications, LLC
3 AS3215 Orange S.A.
3 AS2527 Sony Network Communications Inc.
3 AS22552 eSited Solutions
3 AS211607 Securitytrails, LLC
3 AS12389 PJSC Rostelecom
2 AS9506 Singtel Fibre Broadband
2 AS9319 HCN CHUNGBUK CABLE TV SYSTEMS
2 AS8551 Bezeq International Ltd.
2 AS8048 CANTV Servicios, Venezuela
2 AS7545 TPG Telecom Limited
2 AS7418 TELEFÓNICA CHILE S.A.
2 AS62904 Eonix Corporation
2 AS62160 WEB3 Leaders INC
2 AS58212 dataforest GmbH
2 AS4811 China Telecom (Group)
2 AS47154 HUSAM A. H. HIJAZI
2 AS44592 SkyLink Data Center BV
2 AS42237 w1n ltd
2 AS41436 Kamatera Inc
2 AS398791 GoDaddy.com, LLC
2 AS39501 NGSAS NedaGostarSaba
2 AS38283 CHINANET SiChuan Telecom Internet Data Center
2 AS35916 MULTACOM CORPORATION
2 AS33363 Charter Communications, Inc
2 AS33182 HostDime.com, Inc.
2 AS31898 Oracle Corporation
2 AS26599 TELEFÔNICA BRASIL S.A
2 AS2635 Automattic, Inc
2 AS25369 Hydra Communications Ltd
2 AS2514 NTT PC Communications, Inc.
2 AS22773 Cox Communications Inc.
2 AS22501 Cooperativa Telefonica Carlos Tejedor Ltda.
2 AS212815 Dyjix SAS
2 AS209828 Genc BT Bilisim Teknolojileri Limited Sirketi
2 AS209559 XHOST INTERNET SOLUTIONS LP
2 AS208091 XHOST INTERNET SOLUTIONS LP
2 AS20214 Comcast Cable Communications, LLC
2 AS18779 EGIHosting
2 AS17676 SoftBank Corp.
2 AS17511 OPTAGE Inc.
2 AS17421 Mobile Business Group
2 AS16509 Amazon.com, Inc.
2 AS16232 Telecom Italia S.p.A.
2 AS15895 "Kyivstar" PJSC
2 AS150706 Hong Kong Zhengxing Technology Co., Ltd.
2 AS14618 Amazon.com, Inc.
2 AS142002 Scloud Pte Ltd
2 AS135944 VinhNam Commercial informatics service corporation
2 AS135905 VIETNAM POSTS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS GROUP
2 AS134238 CHINANET Jiangx province IDC network
2 AS12683 PJSC Rostelecom
2 AS1267 WIND TRE S.P.A.
2 AS1257 Tele2 Sverige AB
2 AS12400 Partner Communications Ltd.
2 AS11492 CABLE ONE, INC.
1 AS9976 Namincheon Brodcasting Co., Ltd.
1 AS9845 LG HelloVision Corp.
1 AS9824 JCOM Co., Ltd.
1 AS9697 LG HelloVision Corp.
1 AS9689 SK Broadband Co Ltd
1 AS9595 NTT-ME Corporation
1 AS9316 DACOM-PUBNETPLUS
1 AS9304 HGC Global Communications Limited
1 AS9299 Philippine Long Distance Telephone Company
1 AS9198 JSC Kazakhtelecom
1 AS9050 ORANGE ROMANIA COMMUNICATION S.A
1 AS8612 Tiscali Italia S.P.A.
1 AS8595 OOO WestCall Ltd.
1 AS852 TELUS Communications Inc.
1 AS8473 Bahnhof AB
1 AS8447 A1 Telekom Austria AG
1 AS8374 Polkomtel Sp. z o.o.
1 AS8369 Intersvyaz-2 JSC
1 AS812 Rogers Communications Canada Inc.
1 AS786 Jisc Services Limited
1 AS7713 PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia
1 AS7470 TRUE INTERNET Co.,Ltd.
1 AS7377 University of California, San Diego
1 AS6871 Plusnet
1 AS680 Verein zur Foerderung eines Deutschen Forschungsnetzes e.V.
1 AS6799 Ote SA (Hellenic Telecommunications Organisation)
1 AS64227 CONSOLIDATED TELEPHONE COMPANY
1 AS63961 Bangladesh Research and Education Network (BdREN)
1 AS6327 Shaw Communications Inc.
1 AS61857 SPEEDFAST TELECOM
1 AS6167 Verizon Business
1 AS6147 Telefonica del Peru S.A.A.
1 AS6130 American Internet Services, LLC.
1 AS6128 Cablevision Systems Corp.
1 AS60068 Datacamp Limited
1 AS59477 LIFEPC, s.r.o.
1 AS58541 Qingdao,266000
1 AS58519 Cloud Computing Corporation
1 AS58321 Oxylion S. A.
1 AS58224 Iran Telecommunication Company PJS
1 AS57678 Cat Technologies Co. Limited
1 AS57588 Hayat for Internet & communication LLC
1 AS57044 JSC "ER-Telecom Holding"
1 AS5650 Frontier Communications of America, Inc.
1 AS56478 Hyperoptic Ltd
1 AS56048 China Mobile Communicaitons Corporation
1 AS56047 China Mobile communications corporation
1 AS56046 China Mobile communications corporation
1 AS56042 China Mobile communications corporation
1 AS55720 Gigabit Hosting Sdn Bhd
1 AS55492 Dhaka Fiber Net Limited
1 AS5384 EMIRATES TELECOMMUNICATIONS GROUP COMPANY (ETISALAT GROUP) PJSC
1 AS53153 CINTE Telecom Comercio e Servicos Ltda.
1 AS53006 ALGAR TELECOM S/A
1 AS52936 ISOTELCO LTDA
1 AS52606 BRASILNETS COM. ATAC. DE EQ. INFORMATICA LTDA ME
1 AS52207 JSC "ER-Telecom Holding"
1 AS51852 Private Layer INC
1 AS51570 JSC "ER-Telecom Holding"
1 AS51115 HLL LLC
1 AS5089 Virgin Media Limited
1 AS49893 Bitrace telecom Ltd.
1 AS49202 Kisara LLC
1 AS49100 Pishgaman Toseeh Ertebatat Company (Private Joint Stock)
1 AS48854 team.blue Denmark A/S
1 AS48737 DoraTelekom
1 AS48715 Sefroyek Pardaz Engineering PJSC
1 AS4847 China Networks Inter-Exchange
1 AS48347 JSC Mediasoft ekspert
1 AS4816 China Telecom (Group)
1 AS48090 PPTECHNOLOGY LIMITED
1 AS47890 UNMANAGED LTD
1 AS4788 TM TECHNOLOGY SERVICES SDN. BHD.
1 AS47764 LLC VK
1 AS47583 Hostinger International Limited
1 AS46606 Unified Layer
1 AS4657 StarHub Ltd
1 AS45629 JasTel Network International Gateway
1 AS45458 SBN-ISP/AWN-ISP and SBN-NIX/AWN-NIX
1 AS44724 Octopusnet LTD
1 AS44634 LLC SibSvayzStroy
1 AS43260 DGN TEKNOLOJI A.S.
1 AS42668 Nevalink, LLC
1 AS400328 Intelligence Hosting LLC
1 AS398989 DeepIntent, Inc.
1 AS398722 Censys, Inc.
1 AS3920 ESTOXY OU
1 AS38478 SunnyVision Limited
1 AS38372 RJNET
1 AS38264 National WiMAX/IMS environment
1 AS38096 SK Broadband Co Ltd
1 AS3786 LG DACOM Corporation
1 AS37608 iRENALA
1 AS37517 CV Multimedia SA
1 AS36925 MEDITELECOM
1 AS36493 FIBERNETICS CORPORATION
1 AS36459 GitHub, Inc.
1 AS3605 Guam Cablevision, LLC.
1 AS35562 Kedr Ltd.
1 AS35125 PJSC Rostelecom
1 AS34984 Superonline Iletisim Hizmetleri A.S.
1 AS34622 Bredband i Kristianstad AB
1 AS33915 Vodafone Libertel B.V.
1 AS33668 Comcast Cable Communications, LLC
1 AS33659 Comcast Cable Communications, LLC
1 AS33588 Charter Communications
1 AS3329 VODAFONE-PANAFON HELLENIC TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANY SA
1 AS3303 Swisscom (Schweiz) AG
1 AS3301 Telia Company AB
1 AS328608 Africa on Cloud
1 AS3209 Vodafone GmbH
1 AS31213 PJSC MegaFon
1 AS31133 PJSC MegaFon
1 AS31034 Aruba S.p.A.
1 AS30722 Vodafone Italia S.p.A.
1 AS30036 Mediacom Communications Corp
1 AS29484 Ruhr-Universitaet Bochum
1 AS28573 Claro NXT Telecomunicacoes Ltda
1 AS2856 British Telecommunications PLC
1 AS28294 B S Costa Telecom
1 AS28283 Adylnet Telecom
1 AS28209 Under Servicos de Internet Ltda
1 AS27951 Media Commerce Partners S.A
1 AS27882 Telefónica Celular de Bolivia S.A.
1 AS270719 START NET TELECOM LTDA
1 AS269832 MDS TELECOM C.A.
1 AS269608 VELOSO NET SERV DE COMUNICACAO MULTIDIA EIRELI
1 AS267784 Flyservers S.A.
1 AS266608 Ola Fibra Telecomunicacoes LTDA
1 AS266181 GOLDEN LINK
1 AS263056 INDNET TELECOMUNICACOES LTDA
1 AS26277 ServerPoint.com
1 AS262663 METROFLEX TELECOMUNICACOES LTDA
1 AS262378 Compuservice Empreendimentos Ltda
1 AS262318 Horizons Telecomunicações e Tecnologia S.A.
1 AS2519 ARTERIA Networks Corporation
1 AS2518 BIGLOBE Inc.
1 AS2516 KDDI CORPORATION
1 AS25106 Mobile TeleSystems JLLC
1 AS25019 Saudi Telecom Company JSC
1 AS24961 myLoc managed IT AG
1 AS24700 WEB3 Leaders INC
1 AS24560 Bharti Airtel Ltd., Telemedia Services
1 AS24547 Hebei Mobile Communication Company Limited
1 AS24444 Shandong Mobile Communication Company Limited
1 AS24164 UNION BROADBAND NETWORK
1 AS23724 IDC, China Telecommunications Corporation
1 AS22408 West Ky Networks
1 AS216240 MortalSoft Ltd.
1 AS216167 Skoali SAS
1 AS215862 Taliene De Araujo Souza
1 AS213402 Rahat Telecom LLC
1 AS213149 Telelink Telecommunications Co for Internet services and Information Technology Ltd.
1 AS212913 FOP Hornostay Mykhaylo Ivanovych
1 AS211715 Partlix, Ltd.
1 AS2116 GLOBALCONNECT AS
1 AS211557 TAYNET TEKNOLOJI TICARET LIMITED SIRKETI
1 AS211235 AL-SAHIN AL-SHABALY Co. for Internet Services Ltd
1 AS211056 Amir Hosein Maaref
1 AS210218 Open Fiber S.P.A.
1 AS209711 MUV Bilisim ve Telekomunikasyon Hizmetleri Ltd. Sti.
1 AS209 CenturyLink Communications, LLC
1 AS208258 Access2.IT Group B.V.
1 AS207147 NETCOM GROUP SAS
1 AS206264 Amarutu Technology Ltd
1 AS206216 Advin Services LLC
1 AS206119 Veganet Teknolojileri ve Hizmetleri LTD STI
1 AS20473 The Constant Company, LLC
1 AS202520 SkyPass Solutions Sp. z.o.o.
1 AS202468 Noyan Abr Arvan Co. ( Private Joint Stock)
1 AS201776 Miranda-Media Ltd
1 AS20115 Charter Communications
1 AS19871 Network Solutions, LLC
1 AS197183 Occentus Network SL
1 AS197078 Yarnet Ltd
1 AS19037 AMX Argentina S.A.
1 AS18822 Manquehuenet
1 AS18809 Cable Onda
1 AS18403 FPT Telecom Company
1 AS18144 Energia Communications,Inc.
1 AS18081 Kintetsu Cable Network Co., Ltd.
1 AS18049 Taiwan Infrastructure Network Technologie
1 AS17858 LG POWERCOMM
1 AS17809 VEE TIME CORP.
1 AS17747 SITI NETWORKS LIMITED
1 AS17698 COMMUNITY NETWORK CENTER INCORPORATED.
1 AS17665 ONEOTT INTERTAINMENT LIMITED
1 AS17639 Converge ICT Solutions Inc.
1 AS17488 Hathway IP Over Cable Internet
1 AS17451 BIZNET NETWORKS
1 AS16863 Home Telephone Company, Inc.
1 AS16629 CTC. CORP S.A. (TELEFONICA EMPRESAS)
1 AS16116 Pelephone Communications Ltd.
1 AS15704 XTRA TELECOM S.A.
1 AS15493 "Russian company" LLC
1 AS15169 Google LLC
1 AS151487 Awesomecloud Limited
1 AS149570 Speech Tell Communication Private Limited
1 AS147176 NZ Network Enterprise Co., Ltd.
1 AS142111 Zhejiang Aiyun Network Technology Co Ltd
1 AS141679 China Telecom Beijing Tianjin Hebei Big Data Industry Park Branch
1 AS141480 Haash Media
1 AS141152 BATAAN SPACE CABLE NETWORK INC
1 AS140726 UNICOM AnHui province network
1 AS1403 EBOX
1 AS139752 Multinetwork Cable Television, Inc
1 AS139281 Equinix Korea LLC
1 AS138968 rainbow network limited
1 AS138152 YISU CLOUD LTD
1 AS138025 RBC Cable Master System
1 AS137941 Mabuhay Cable TV Inc
1 AS137718 Beijing Volcano Engine Technology Co., Ltd.
1 AS137443 Anchnet Asia Limited
1 AS136052 PT Cloud Hosting Indonesia
1 AS135161 GMO-Z com NetDesign Holdings Co., Ltd.
1 AS13490 Buckeye Cablevision, Inc.
1 AS13489 EPM Telecomunicaciones S.A. E.S.P.
1 AS134810 China Mobile Group JiLin communications corporation
1 AS134765 CHINANET Yunnan province IDC1 network
1 AS134762 CHINANET Liaoning province Dalian MAN network
1 AS134756 CHINANET Nanjing Jishan IDC network
1 AS134420 Chongqing Telecom
1 AS134143 Professional Data Kinetics Pty Ltd
1 AS133676 Precious netcom pvt ltd
1 AS133159 Mammoth Media Pty Ltd
1 AS132335 LeapSwitch Networks Pvt Ltd
1 AS13188 CONTENT DELIVERY NETWORK LTD
1 AS131414 Long Van Soft Solution JSC
1 AS131353 NhanHoa Software company
1 AS131090 CAT TELECOM Public Company Ltd,CAT
1 AS12897 ENTEGA Medianet GmbH
1 AS12874 Fastweb SpA
1 AS12849 Hot-Net internet services Ltd.
1 AS12735 TurkNet Iletisim Hizmetleri A.S.
1 AS12730 PJSC Rostelecom
1 AS12494 OOO "Post ltd"
1 AS12322 Free SAS
1 AS1221 Telstra Corporation Ltd
1 AS11830 Instituto Costarricense de Electricidad y Telecom.
1 AS11351 Charter Communications Inc
1 AS10796 Charter Communications Inc
1 AS10269 Belize Telemedia LimitedInterpretation of Blocked Scans by Organization
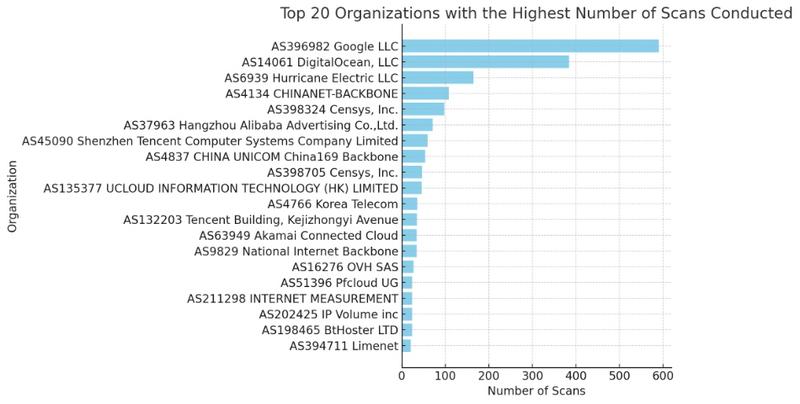
- 1. Google LLC (AS396982)
- Number of occurrences: 590
- Implication: Significant activity from IP addresses associated with Google, indicating potential use of Google services for network scanning or misuse of their PaaS GCP platform.
- 2. DigitalOcean, LLC (AS14061)
- Number of occurrences: 384
- Implication: High scanning activity from this cloud organization, suggesting either legitimate services or potentially compromised cloud instances.
- 3. Hurricane Electric LLC (AS6939)
- Number of occurrences: 165
- Implication: Notable presence of scans from this Internet service provider, possibly indicating abuse of its services for scanning activities.
- 4. Chinese Organizations
- Number of occurrences:
- CHINANET-BACKBONE (AS4134): 108
- Hangzhou Alibaba (AS37963): 71
- Tencent (AS45090): 59
- CHINA UNICOM (AS4837): 54
- Other Chinese organizations with significant occurrences
- Implication: Scanning activities emanating from major Chinese corporations, reflecting either legitimate operations or abuse of their networks.
- Number of occurrences:
- 5. Censys, Inc. (AS398324, AS398705)
- Number of occurrences: Total of 145
- Implication: Censys, a data security-focused company, appears engaged in scanning activity, likely in a security research context.
- 6. OVH SAS (AS16276) and Other Hosting Providers
- Implication: Scans from OVH and other hosting providers may indicate either legitimate services or abuse of hosting resources.
- 7. Diversity of Global Sources
- Implication: The presence of organizations from many countries (e.g., KR, IN, RU, JP, VN) shows a diversity in the geographical origin of scans, which may reflect a wide range of intentions and practices.
- 8. Scanning Activities by ISPs and Telecommunications Companies
- Examples: Korea Telecom (AS4766), NTT Communications (AS4713)
- Implication: These ISPs and telecommunications companies may be involved in scans for maintenance, security, or other legitimate activities.
These statistics underscore the importance of ongoing monitoring and protection against potentially malicious scanning activities. The diversity of sources, ranging from cloud service providers to major telecommunications companies, illustrates the complexity of the online security ecosystem.
Scans by City
Results
314 San Francisco
218 London
210 North Charleston
107 Chicago
103 Amsterdam
77 Pleasanton
75 Frankfurt am Main
62 Kingsburg
57 Shenzhen
55 São Paulo
50 Shanghai
48 Taichung
45 Brussels
42 Beijing
38 Council Bluffs
33 Nanjing
32 Hangzhou
25 Hopel
24 Thetford
22 Paris
22 Hong Kong
21 Singapore
21 Santa Clara
20 San Diego
18 Morris Plains
18 Los Angeles
17 Moscow
17 Ann Arbor
16 Tokyo
16 Sofia
16 North Bergen
15 Seoul
14 Shenyang
14 Palo Alto
12 Chengdu
11 Wuhan
11 Taiyuan
10 Taipei
10 Sydney
10 Stockholm
10 San Mateo
10 Ho Chi Minh City
10 Clifton
10 Bangkok
9 Qingdao
9 Milan
9 Kunming
9 Jakarta
9 Fremont
9 Chongqing
8 Saint Petersburg
8 Roubaix
8 Changchun
7 Phoenix
7 New York City
7 Lille
7 Istanbul
7 Beauharnois
6 Zhengzhou
6 Zhangjiakou
6 Warsaw
6 Toronto
6 Dallas
6 Buffalo
6 Ashburn
6 Aachen
5 Vilnius
5 Mumbai
5 Mangalagiri
5 Harbin
5 Hanoi
5 Haarlem
5 Changsha
5 Bengaluru
4 Thiruvananthapuram
4 Tehran
4 Santiago
4 Richardson
4 Las Vegas
4 Incheon
4 Düsseldorf
4 Berlin
4 Atlanta
3 Thoothukudi
3 Shanxi
3 Seattle
3 San Jose
3 Reston
3 Prague
3 Nürnberg
3 Montréal
3 Lagos Island
3 Kollam
3 Hefei
3 Gwangju
3 Guiyang
3 Guangzhou
3 General Alvear
3 Chennai
3 Caracas
3 Busan
3 Banqiao
3 Baghdad
2 Zürich
2 Xining
2 Vinh
2 Vienna
2 Utsunomiya
2 Timişoara
2 Tianjin
2 The Dalles
2 Suwon
2 Shijiazhuang
2 Seongnam-si
2 Rio de Janeiro
2 Pyatigorsk
2 Portsmouth
2 Philadelphia
2 Palermo
2 Olathe
2 Nanchang
2 Mito
2 Miryang
2 Mar del Plata
2 Kolkata
2 Kaunas
2 Jalandhar
2 Hunan
2 Hoàn Kiếm
2 Hazāribāgh
2 Gruzino
2 Göteborg
2 Fuzhou
2 Fengshan
2 Dubai
2 Doddaballapura
2 Dhaka
2 Contai
2 Coimbatore
2 Chinch'ŏn
2 Cheongju-si
2 Central
2 Buenos Aires
2 Ankara
1 Đồng Hới
1 Ōtsu
1 Şişli
1 Ōbu
1 Zolotonosha
1 Zhongxing New Village
1 Zhenjiang
1 Zhanjiang
1 Zapolyarnyy
1 Yongsan-dong
1 Yogyakarta
1 Yingkou
1 Yilan
1 Yigo Village
1 Yesan
1 Yelets
1 Yekaterinburg
1 Yecheon
1 Yaroslavl
1 Yangsan
1 Yangquan
1 Xi’an
1 Wrocław
1 Winter Park
1 Whittier
1 Waterloo
1 Waterford
1 Wakefield
1 Waegwan
1 Volgograd
1 Vladivostok
1 Vigia
1 Veranópolis
1 Vancouver
1 Valencia
1 Una
1 Ulsan
1 Uberlândia
1 T’aebaek
1 Tyumen
1 Tula
1 Tuguegarao
1 Trelew
1 Tilburg
1 Thessaloníki
1 The Acreage
1 Thái Nguyên
1 Tempe
1 Tefé
1 Tân An
1 Takasaki
1 Tainan
1 Sylvania
1 Surat Thani
1 Stratford-upon-Avon
1 Strasbourg
1 Southend-on-Sea
1 South Riding
1 Smolensk
1 Simferopol
1 Shulin
1 Shaoxing
1 Sevastopol
1 Serpong
1 Sergiyev Posad
1 Sejong
1 Secaucus
1 Satellite Beach
1 Sardinal
1 Sapporo
1 Santa Monica
1 Santa Fe
1 San Pedro
1 Samut Songkhram
1 Sainte-Geneviève-des-Bois
1 Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines
1 Ryazan’
1 Rondonópolis
1 Rome
1 Riverside
1 Rishon LeTsiyyon
1 Raebareli
1 Quận Bốn
1 Puerto Madryn
1 Provo
1 Praia
1 Poznań
1 Pohang
1 Petaling Jaya
1 Pathanāmthitta
1 Passos
1 Pasig City
1 Paripark
1 Pardīs
1 Panvel
1 Panama City
1 Palm Beach Gardens
1 Padova
1 Oslo
1 Osaka
1 Okayama
1 Novosibirsk
1 Nova Iguaçu
1 Ningbo
1 Niagara Falls
1 New Delhi
1 Neietsu
1 Neapoli
1 Naples
1 Nanning
1 Nagoya
1 Murray
1 Munich
1 Motoyoyogichō
1 Morro
1 Monterrey
1 Mokotów
1 Minsk
1 Minatitlán
1 Michelstadt
1 Miaoli
1 Melbourne
1 Massy
1 Masan
1 Masaguisi
1 Marinilla
1 Manila
1 Magnitogorsk
1 Mafra
1 Mâcon
1 Machida
1 Macapá
1 Luxembourg
1 Lutsk
1 Ludhiāna
1 Liverpool
1 Linfen
1 Largo
1 La Paz
1 Kōriyama
1 Kyiv
1 Kurashiki
1 Köln
1 Koesan
1 Kobe
1 Kislovodsk
1 Kimhae
1 Kharkiv
1 Kalispell
1 Jinrongjie
1 Jinan
1 Jiaxing
1 Jerusalem
1 Jeju City
1 Isparta
1 Isfahan
1 Indianapolis
1 Imperatriz
1 Iksan
1 Ikoma
1 Ichikawa-minami
1 Hwawŏn
1 Huzhou
1 Huizhou
1 Hrochoť
1 Honolulu
1 Hohhot
1 Hitachi-Naka
1 Hisar
1 Hicksville
1 Heyuan
1 Hatsudai
1 Harston
1 Hammarslund
1 Hamburg
1 Halesowen
1 Haikou
1 Haifa
1 Hadano
1 Gumi
1 Guanajuato
1 Guadalajara
1 Groningen
1 Greenford
1 Goose Creek
1 Goochland
1 Gold Coast
1 Goiânia
1 Gifu-shi
1 Giddalūr
1 Ghāziābād
1 Genoa
1 Gangseo-gu
1 Fukuyama
1 Fontana
1 Florence
1 Feltham
1 Faisalabad
1 Essen
1 Englewood Cliffs
1 El Pedregal
1 Ekibastuz
1 Eilat
1 Ecoporanga
1 Douliu
1 Doral
1 Derval
1 Dammam
1 Daejeon
1 Da Nang
1 Curitiba
1 Cormano
1 Çorlu
1 Córdoba
1 Corcuera
1 Columbus
1 Ciudad López Mateos
1 Cirebon
1 Cincinnati
1 Cibinong
1 Chư Ty
1 Chiang Mai
1 Chernihiv
1 Changde
1 Chandīgarh
1 Chandler
1 Ceres
1 Castiglione delle Stiviere
1 Casablanca
1 Cambridge
1 Cabanatuan City
1 Bursa
1 Burnaby
1 Bucharest
1 Bryansk
1 Brampton
1 Boydton
1 Bologna
1 Bogotá
1 Bochum
1 Boardman
1 Bhopāl
1 Belford Roxo
1 Balanga
1 Baku
1 Atlantic City
1 Ashdod
1 Antananarivo
1 Anseong
1 Andong
1 Anderson
1 Amritsar
1 Akashi
1 Aitkin
1 Ahvaz
1 Ahmedabad
1 Adelaide
1 AabenraaInterpretation of Blocked Scans Statistics by City
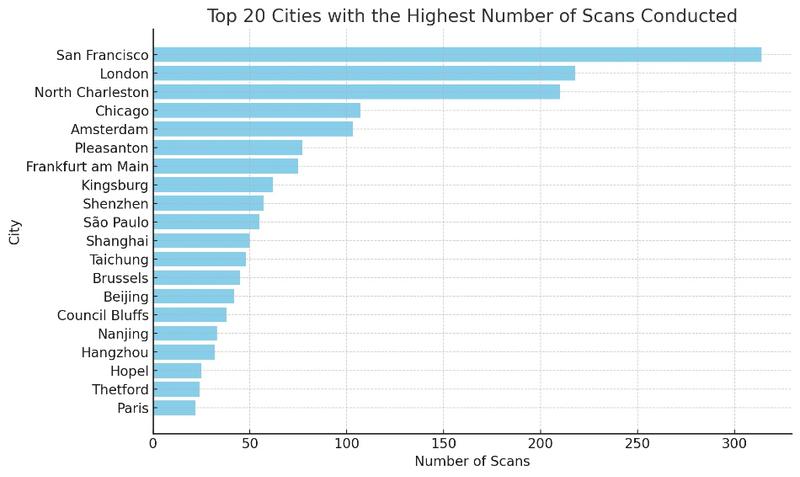
- 1. San Francisco (314 Occurrences)
- Implication: Significant activity from this technologically advanced city, likely reflecting the use of services based in Silicon Valley.
- 2. London (218 Occurrences)
- Implication: Strong activity from this global metropolis, suggesting scanning operations from companies based in London or using services hosted there.
- 3. North Charleston (210 Occurrences)
- Implication: A surprising number of scans from this city, possibly indicating the presence of cloud service infrastructures or other technology companies.
- 4. Chinese Cities (Shenzhen, Shanghai, Beijing, etc.)
- Total Occurrences: Over 150
- Implication: Significant scans emanating from several major Chinese cities, illustrating the breadth of technological and digital presence in China.
- 5. Amsterdam (103 Occurrences)
- Implication: With its cloud service infrastructure and data centers, Amsterdam is a notable source of scans.
- 6. Frankfurt am Main (75 Occurrences)
- Implication: High activity in this German city, known for its data centers and key role in European networks.
- 7. Diversity of Global Sources
- Implication: The variety of cities (such as Seoul, Tokyo, Paris, Moscow) indicates a global distribution of scan sources, reflecting the global nature of online activity and potential threats.
- 8. Specific Activities of Certain Cities
- Examples: São Paulo, Singapore, Santa Clara
- Implication: These cities, known for their concentration of technology companies, show scanning activity that may be attributed to legitimate research or network abuses.
These statistics highlight the geographical diversity of scanning activities and underscore the importance of cybersecurity measures. The presence of scans from major technological and financial cities indicates that these regions are hotspots for online activities, necessitating increased vigilance for network protection.
Conclusion
Securing your Nginx server with Fail2ban and UFW is a crucial step in protecting your data and infrastructure against increasingly sophisticated cyber attacks. In this article, we have seen how Fail2ban and UFW can be used together to form a robust barrier against attacks, by combining the detection and banning of malicious IP addresses with rigorous management of network traffic.
Implementing these tools is just the beginning of an ongoing security process. It is essential to keep these systems updated, regularly adjust configurations in response to new threats, and continuously monitor logs for intrusion attempts. Data analysis clearly demonstrates the importance of these tools in detecting and blocking a multitude of unauthorized access attempts from around the world.
Finally, keep in mind that security is an evolving practice. Threats are constantly changing, and our defense methods must adapt accordingly. Do not hesitate to explore new tools, share your knowledge with the community, and stay informed of the latest trends in cybersecurity.
Stay safe, stay secure!




