
Monitoring and Audit in AWS - CloudWatch, X-Ray et CloudTrail
One of the important aspects when deploying an application in the Cloud is monitoring and supervision in order to ensure that all application services work well and to be able to react in the event of a failure.
AWS offers several tools to accomplish these two tasks:
- AWS CloudWatch
- Metrics: collection of metrics integrated into AWS services and those of your application
- Logs: collects and stores log files (logs)
- Events: sends notification in response to certain events
- Alarms: sets activation thresholds (alarms) that trigger an action
- AWS X-Ray
- Help in the analysis and debugging of applications even those distributed
- Graphically produces the path of a query and the components it passes through with the associated errors
- AWS CloudTrail
- Monitoring calls to APIs
- Compliance Analysis
- Operational Audit
- AWS CloudWatch Metrics
- AWS CloudWatch Logs
- CloudWatch Metric Filters and CloudWatch Alarms
- CloudWatch Events and Amazon EventBridge
- AWS X-Ray
- AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudWatch Metrics
Metrics are data about the activity of your systems. By default, many AWS services provide metrics.
- Free metrics have a Frequency of 5 min, it is possible to reduce it by activating the Detailed Monitoring option but for an additional cost
- Metrics are time-stamped
- Metrics are grouped first by namespace, then by the different combinations of dimensions (resource attributes) within each namespace. For example, you can display all EC2 metrics, EC2 metrics grouped by instance, or EC2 metrics grouped by auto-scaling group.
- Only the AWS services you use send metrics to Amazon CloudWatch.
- For a list of AWS services that send metrics to CloudWatch, see AWS services that publish CloudWatch metrics. From this page you can also see the metrics and dimensions published by each of these services.
Custom Metrics
You can publish your own metrics (Custom Metrics) in CloudWatch using the put-metric-data command on the AWS CLI or PutMetricData API:
- Periodicity can be Standard (1 min or more) or High resolution (1, 5, 10 or 30s)
- Up to 10 dimensions can be defined
AWS CloudWatch Logs
General
- CloudWatch can log most AWS services and applications that use the SDK
- There is a Log Group that represents the application and a Log Stream that represents each service
- There is an expiry policy (30, 90 days, never, …)
- These logs can be exported to S3 (to be saved) or to a Elastic Search Cluster for analysis
- Specific IAM permissions are required to allow CloudWatch to retrieve logs and they can be encrypted using AWS KMS (Log Group level)
CloudWatch Log Agent
For EC2 instances and on-premise servers, it is necessary to install an Agent.
There are two versions:
- CloudWatch Log Agent: An older version that can only handle logs
- CloudWatch Unified Agent: The latest version that can handle logs but also detailed metrics on CPU, RAM, Disk, NetStat, Process, Swap,… of the server and SSM Parameter Store
CloudWatch Metric Filters and CloudWatch Alarms
- CloudWatch Metric Filters can filter logs with expressions (IP, RegExp,…) to trigger Alarms
- CloudWatch Alarm can trigger notifications to an ASG, AWS SNS, EC2 Action based on a metric
CloudWatch Events and Amazon EventBridge
- CloudWatch Events :
- Reacts from rules to what a service does (terminating an instance,…)
- Creates an event in the form of a JSON message containing what caused it to react
- Can interface to AWS SQS, SNS or Kinesis
- Amazon EventBridge:
- It takes into account 3 Event Bus:
- Default Event Bus for AWS Services
- Partner Event Bus for SaaS Services and AWS Partners
- Custom Event Bus for your application
- It also works with rules just like CloudWatch Event
- EventBridge can deduce the structure of the message and the Schema Registry generates the application code required for your application
- It takes into account 3 Event Bus:
To be noted
CloudWatch Events and Amazon EventBridge are based on the same AWS infrastructure but Amazon EventBridge is the latest version and offers more features than CloudWatch Events.
AWS X-Ray
- AWS X-Ray is a service that collects data requests for your applications. It also allows to display and filter them in order to identify problems or optimization possibilities.
- For any traced request in your application, you can see detailed information not only on the request and response, but also on the calls your application makes to the downstream AWS resources, microservices, databases and HTTP Web APIs.
How it works
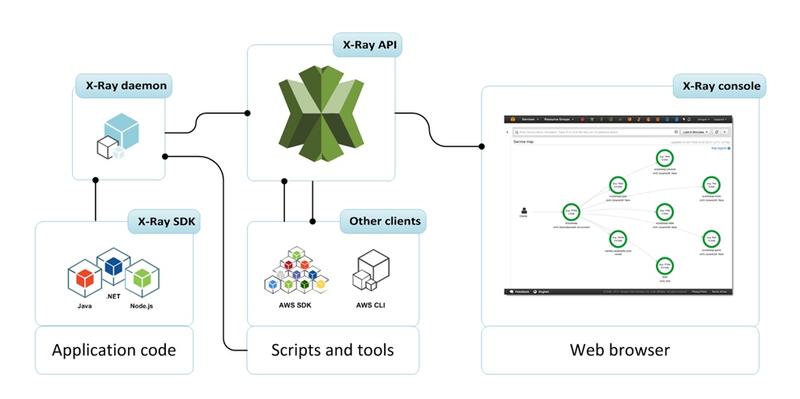
- Each component involved in the request sends a trace to the X-Ray API:
- The application code by integrating the X-Ray SDK specific to its language (supported Java, Node.js, .NET,…) and the X-Ray Daemon installed on the server
- Scripts via AWS SDK or AWS CLI through X-Ray Daemon
- Some AWS services automatically if *option is enabled, except in special cases for EC2 and On-Premise
- All requests can be sent or only a sample
- Requires IAM authorization and is encrypted by AWS KMS
X-Ray SDK
The X-Ray SDK integration requires some changes to the application code.
Example of a Java application
- Dependency Management
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-bom</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-apache-http</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-aws-sdk</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-aws-sdk-instrumentor</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-sql-postgres</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-xray-recorder-sdk-sql-mysql</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- DynamoDB Client
import com.amazonaws.xray.AWSXRay;
import com.amazonaws.xray.handlers.TracingHandler;
public class SessionModel {
private AmazonDynamoDB client = AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(Constants.REGION)
.withRequestHandlers(new TracingHandler(AWSXRay.getGlobalRecorder()))
.build();
private DynamoDBMapper mapper = new DynamoDBMapper(client);X-Ray Daemon
- The X-Ray Daemon is an application that listens to traffic on port UDP 2000, collects data from Segments and transmits it to the API X-Ray
- It is already integrated with many AWS services but needs to be installed on EC2 instances or On-Premise servers
EC2 instances of an ECS cluster
There are 2 possibilities for integrating the X-Ray Daemon:
- Deploy a Daemon container amazon/aws-xray-daemon on each EC2 instance
- Create SideCar container containing an image of the X-Ray Daemon and an image of the application code
AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail is an AWS service that assists you in the governance, compliance and operational and security audit of your AWS account:
- Each action taken by a user, role or AWS service is recorded as event in CloudTrail.
- Events include actions taken in the AWS management console, the AWS CLI and the AWS SDK and API.
CloudTrail is enabled by default on your AWS account
CloudTrail Trail
- Only 90 last days of activity in your AWS account is saved
- Create a Trail in CloudTrail to archive, analyze and react to changes in your AWS resources:
- A Trail is a configuration that allows to send the activity recorded by CloudTrail on a S3 Bucket
- You can also deliver and analyze events in CloudWatch Logs and CloudWatch Events
- A Trail is applied, by default, on all regions but can be applied on only one
CloudTrail Events
A Event in CloudTrail is the record of an activity. They are categorized into 3 types:
- Management Events:
- Provides information on management operations performed on an AWS account
- Configured by default
- Examples: IAM operations, recording devices such as a VPC, creating Trail in CloudTrail Logs, …
- Data Events:
- Provides information on operations performed on or in a resource
- Not active by default because it produces a very large amount of Events
- Examples: Amazon S3 Get/Put/Delete, AWS Lambda function activity, Amazon DynamoDB Get/Put/Delete,…
- Insights Events:
- Capture unusual activity from an AWS account
- Disabled by default
- Examples: any use that differs significantly from typical account usage patterns
EventBridge Integration
Integration from CloudTrail to EventBridge allows automated actions to be launched in response to events on API calls (currently at a Region level)




